Bat Ears: Nature’s Incredible Sound Detection System
Bats are fascinating creatures known for their nocturnal habits and unique ability to navigate using echolocation. One of their most remarkable features is their bat ears, which play a crucial role in their survival. In this article, we’ll explore the anatomy, function, and incredible adaptations of bat ears while keeping SEO best practices in mind.
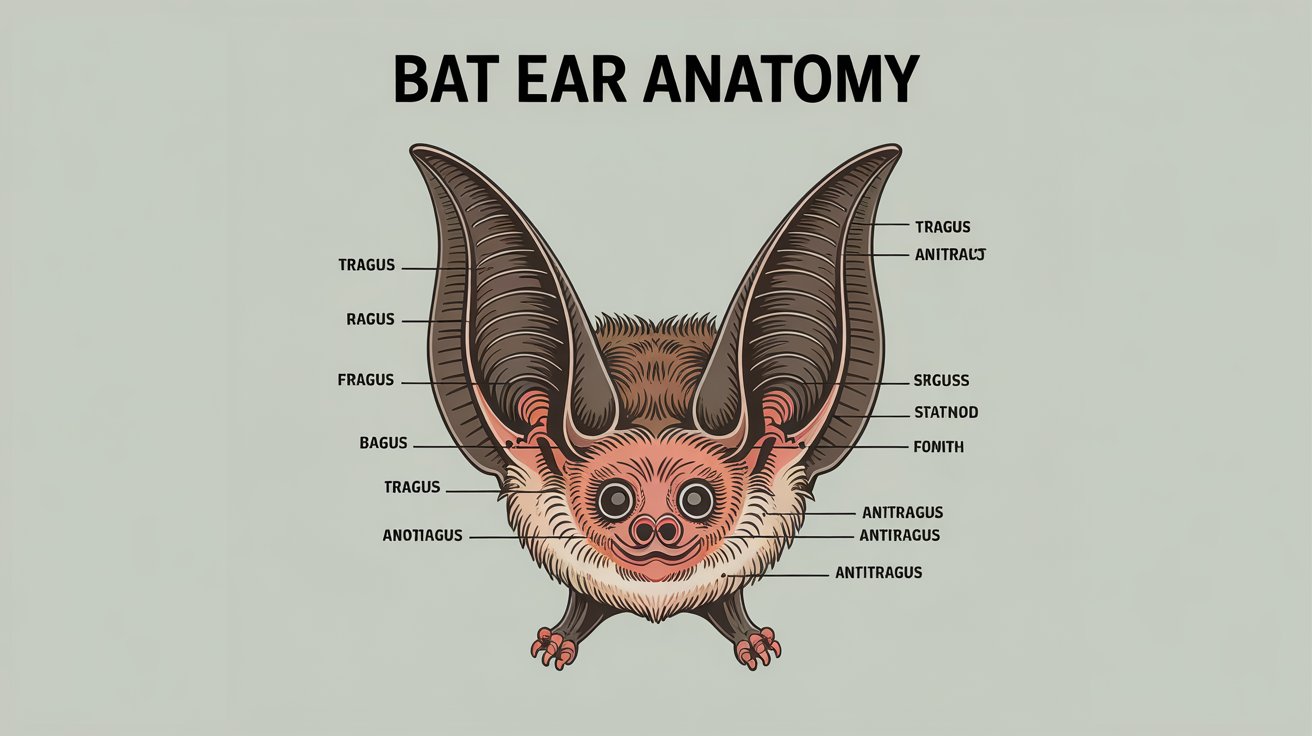
Anatomy of Bat Ears
Bat ears are highly specialized, varying in shape and size depending on the species. Key components include:
- Pinna (Outer Ear): Large and funnel-shaped to capture sound waves efficiently.
- Tragus: A small flap that helps in directing sound into the ear canal.
- Ear Canal: Transmits sound vibrations to the eardrum.
- Cochlea: Converts sound waves into nerve signals for the brain to interpret.
Some bats, like the long-eared bat, have exceptionally large ears to detect faint sounds, while others rely on precise frequency modulation.
How Bat Ears Work in Echolocation
Bats emit high-frequency sounds (ultrasound) that bounce off objects, returning as echoes. Their ears process these echoes to:
- Determine Distance: Time delay between sound emission and echo return.
- Identify Shape & Size: Variations in echo patterns.
- Avoid Obstacles: Navigate in complete darkness.
This biological sonar system is so precise that bats can detect objects as thin as a human hair!
Unique Adaptations of Bats’ Ears
- Mobility: Some bats can move their ears independently to pinpoint sound sources.
- Frequency Sensitivity: Different species hear varying frequency ranges for hunting specific prey.
- Noise Filtering: Bats can distinguish their calls from background noise.
FAQs About Bat Ears
1. Why do bats have such large ears?
Large ears enhance sound collection, which is crucial for echolocation and hunting insects in the dark.
2. Can all bats hear the same frequencies?
No, different bat species detect varying frequency ranges based on their ecological needs.
3. How do Bats’ Ears help in navigation?
The process echoes from emitted sounds, allowing bats to “see” with sound.
4. Do Bats’ ears have any predators?
Some predators, like owls, exploit bats’ reliance on sound, but bats have evolved evasive maneuvers.
Conclusion
Bats’ ears are a marvel of evolutionary adaptation, enabling these nocturnal mammals to thrive in darkness. Their sophisticated echolocation system highlights nature’s ingenuity. Understanding Bats’ ears not only fascinates biologists but also inspires advancements in sonar and hearing technology.
Stay tuned to Earth Breeze for more intriguing insights into the wonders of nature!